Question
What materials are used to create GMOs? How will this technology be changed or adapted in the future?
Submitted by: Anna Hansen
Answer
Expert response from Community Manager
Moderator for GMOAnswers.com
Tuesday, 20/02/2018 13:11
Dr. Larry Gilbertson, PhD, Genomics Strategy Lead at Monsanto, explains how GMOs are “created” or made exactly, answering a lot of common questions about this process in this post. Watch as he discusses GMOs in this video.

Steve Savage, Consultant, Savage & Associates, explains what the future of GMOs may be like in this response.
Also, this response by Qiudeng Que, PhD, Group Leader of Crop Transformation and Analysis at Syngenta Crop Protection, discusses the scientific advancements that GMOs undergo.
On average, GMOs take 16.5 years and $115 million of research and development before they are “created,” otherwise known as coming to market. We’ve created the infographic below that outlines this process in more detail:

GMO is a general term that is used to describe a genetic variation that has occurred, which not only happens in nature, but humans have been doing this through selective breeding for more than thousands of years. When people refer to Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs), they are referring to precision plant breeding using genetic engineering. It allows plant breeders to take a desirable trait (like resistance to drought, insects, weeds, and disease) from one plant or organism and transfer it to the plant they want to improve, as well as make a change to an existing trait in a plant they are developing. You may have also heard of agricultural biotechnology or biotech seeds. These are terms that may be used to refer to the same thing – a genetically modified organism (GMO).
Genetic Engineering is just one form of a breeding technique used in food production. There are a number of methods used in food production including cross breeding, hybridization and mutagenisis. See the below infographic for details about each of these modern methods.
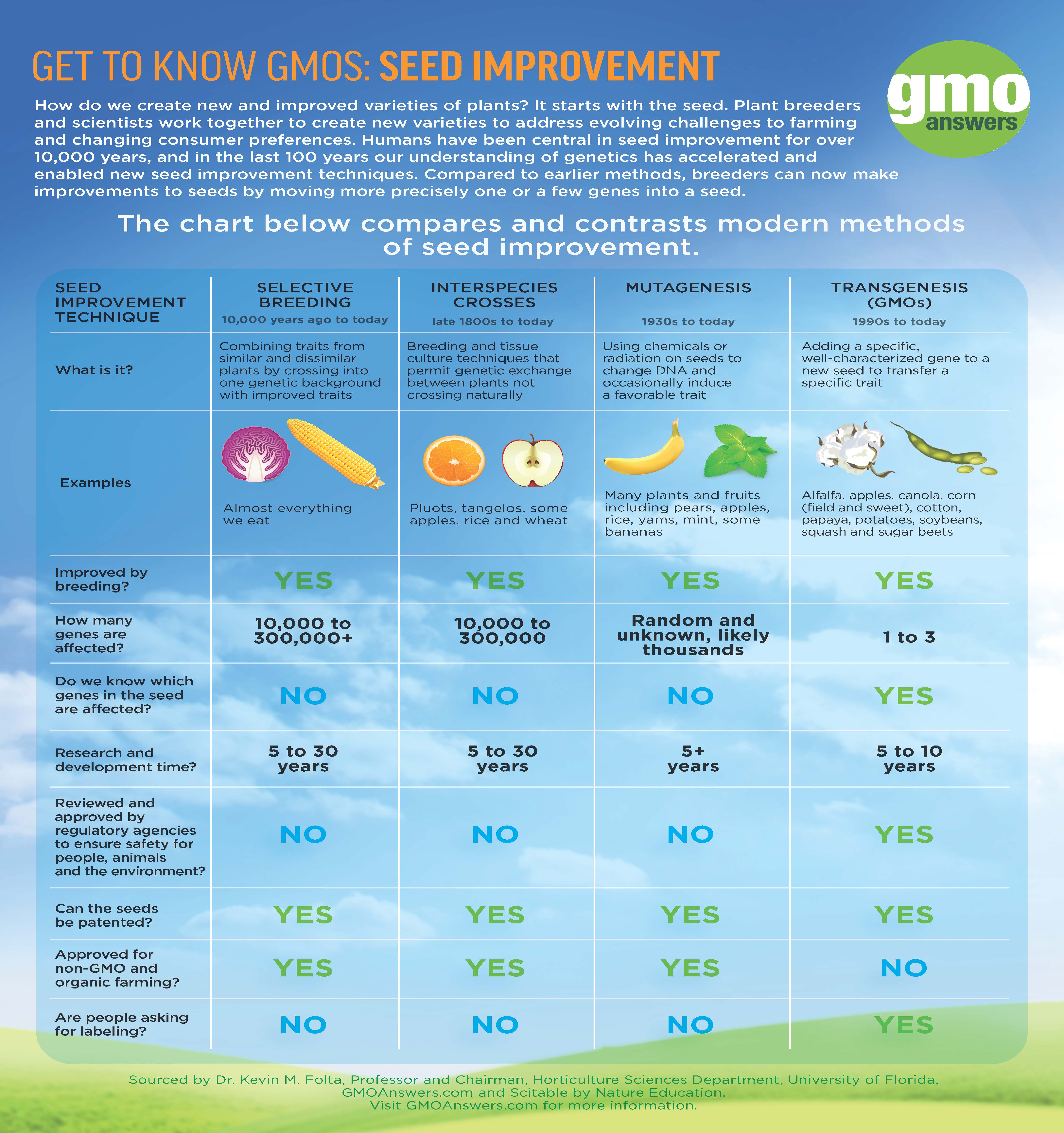
There are currently 10 GMO crops commercially available today: sweet and field corn, soybeans, cotton, canola, alfalfa, sugar beets, papaya, potato, summer squash and apples. These 10 are the only GMO crops that are commercially available, but it is also important to note that many of these crops are ingredients in other types of food you may find in your local grocery store.
For a more in-depth explanation of what GMOs are and why they are created, we encourage you to read more about them here. This post answers additional tough questions surrounding GMOs and better explains the reason biotechnology is incorporated into agriculture.
If you have any other questions about GMOs or biotechnology, please ask!
